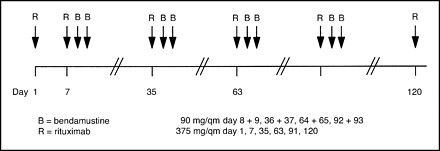
Bendamustine + Rituximab
Mantle cell lymphoma, Indolent NHL
Bendamustine 90 mg/m2 day 2, 3
Rituximab 375 mg/m2 day 1
Schema
Reference
Bendamustine Plus Rituximab Is Effective and Has a Favorable Toxicity Profile in the Treatment of Mantle Cell and Low-Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Mathias J. Rummel Journal of Clinical Oncology, Vol 23, No 15 (May 20), 2005: pp. 3383-3389
PURPOSE: The aim of this multicenter-study was to evaluate the progression-free survival, response rate and toxicity of the combination of bendamustine and rituximab (BR) in patients with mantle cell or low-grade lymphomas in first to third relapse or refractory to previous treatment.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: A total of 245 courses (median, four courses per patient) were administered to 63 patients. Bendamustine was given at a dose of 90 mg/m2 as a 30-minute infusion on days 1 and 2, combined with 375 mg/m2 rituximab on day 1, for a maximum of four cycles every 4 weeks. Histologies were 24 follicular, 16 mantle cell, 17 lymphoplasmacytoid, and six marginal zone lymphoma.
RESULTS: Fifty-seven of 63 patients responded to BR, corresponding to an overall response rate of 90% (95% CI, 80% to 96%) with a complete remission rate (CR) of 60% (95% CI, 47% to 72%). The median time of progression-free survival was 24 months (range, 5 to 44+ months), and the median duration of overall survival has not yet been reached. In mantle cell lymphomas, BR showed a considerable activity, achieving a response rate of 75% (95% CI, 48% to 93%) with a CR rate of 50%. Myelosuppression was the major toxicity, with 16% grade 3 and 4 leukocytopenia. Thrombocytopenia was rare, with only 3% grade 3 and 4.
CONCLUSION: These results demonstrate that the BR combination is a highly active regimen in the treatment of low-grade lymphomas and mantle cell lymphomas.